How many times have you encountered technology in the real world, and wondered what the purpose was? It seems to have been deployed just because it could be. I know I have. The Internet of Things (IoT) can have large societal benefits, when applied purposefully. The GHC session presented by PwC strategy consultant Karla Mendez, entitled Creating Shared Value with IoT Solutions shone a light on companies who incorporate the idea of Shared Value into their technology solutions.
The idea of Shared Value is characterized by Harvard business school professors Michael E. Porter Mark R. Kramer as “a new way for companies to achieve economic success” by finding business value in social problems [1].
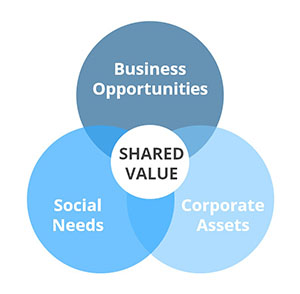
Karla, who took the Shared Value course at Harvard, presented several examples of businesses using IoT to provide a societal need. When businesses position their products as providing Shared Value, a cynic can perceive this as corporate branding that hinges on pandering. Some ways that differentiate companies who have Shared Value at their core are (among other things):
- Placing social good on par with profit as a core value
- Make those values publicly accessible and transparent
- Weaving those values into the thread of all aspects of operations, as an example: sourcing materials only from suppliers that align with that (social good) value
Farm in a Box
I was late to the session, so I didn’t get to hear from the presenter directly about this company. I did find them online and am glad that I did! They market themselves as an “off-grid toolkit for sustainable agriculture.” You can read more about them here. They have their sustainable development goals right on the front of their website!

Intelligent White Boards
An IoT enabled White Board can be deployed in classrooms, and as a teacher writes on the board, it is synced with a corresponding student display, and also allows the student to review the lessons outside of the classroom. Another added benefit is that the teacher gets real-time feedback — doing a quick pop quiz to gauge understanding, can help the teacher adjust when a given topic is not well understood and helps students stay on track for learning. This improves the quality of education. EdTech companies are on the rise, and use the data collected on improved student learning to demonstrate their value. The specific solution referenced in this example, was developed by SMART.
Smart Lighting
The value proposition for smart lighting is that if we can reduce energy use and consumption, we reduce our carbon footprint. Lighting fixtures with IoT sensors can turn off automatically, report when there is an issue (using excess energy). This also reduces energy cost. In the hospitality industry, installing IoT enabled lighting fixtures in hotel rooms can save an estimated $300 per year, per room; the same could be done with heating and cooling. One company providing IoT enabled smart lighting is the presenter’s company: PwC Connected solutions.
Homeless Tracking
There are more than half a million homeless Americans, and only 65% of them are in shelters. This leaves a quarter million people on the streets without resources. Where can IoT help? If we could assess where homeless people are in order to target locations for shelters and other resources, the government could better plan for and reduce homelessness. One solution in this space is digital kiosks. Kiosks could help homeless individuals search for and find resources, like housing. In the Phoenix area, I have seen donation meters. There was not a specific company identified as providing a solution in this space, but with a quick internet search I found that cities like New York and San Francisco are implementing innovative technology to track and align services for their homeless population. I also found an interesting article about LinkNYC, a company that converted old payphones to internet kiosks, but the results were not as rosy as originally intended.
I work for a corporation, and there is an entire branch of the company devoted to social responsibility. It is my hope that as a society, when we learn how our actions impact the world around us, we evolve the way we do business to eliminate negative impacts, not purely for the profit motive, but, because it is the right thing to do.
Recommended Reading:
A few articles I came across that show technology for societal good at work, and one illustrating the unintended consequences.